Payment gateway
What is a payment gateway?
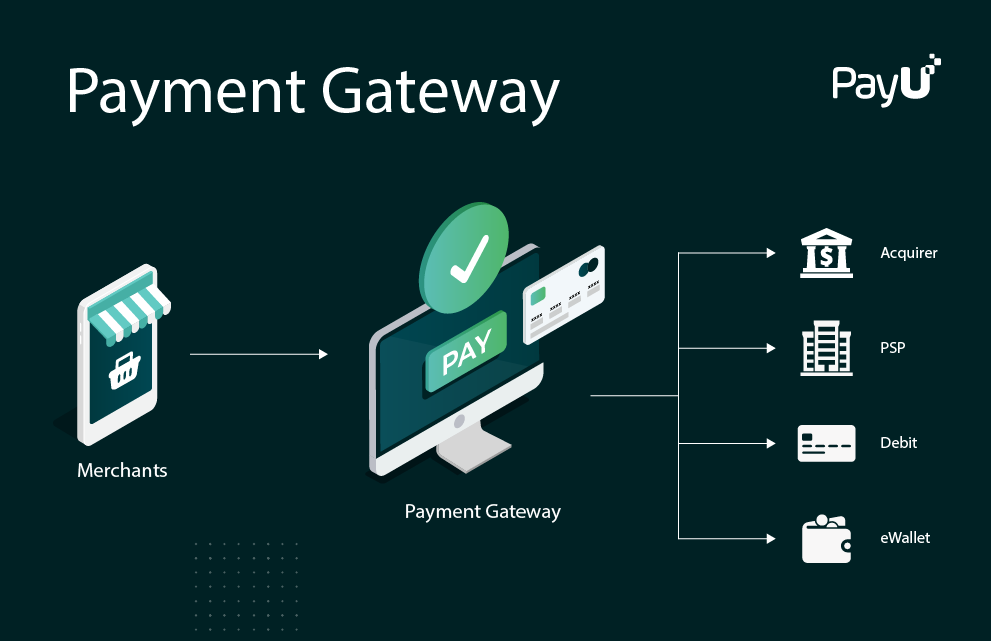
A payment gateway is a software application that processes transactions between a merchant and a customer's payment processor. When a customer places an order on a merchant's website and selects a payment method, the payment gateway processes the transaction and ensures that the funds are transferred securely from the customer to the merchant. Payment gateways also perform other tasks such as authorization and fraud detection to help ensure the security of online transactions. Some popular payment gateways include PayPal, Stripe, and Authorize.net.
How do payment gateways work technically?
When a customer places an order on a merchant's website, the payment gateway performs several tasks to process the transaction:
The payment gateway receives the transaction request from the merchant's website and sends it to the payment processor.
The payment processor verifies the customer's payment method and checks for sufficient funds.
If the payment is approved, the payment processor sends an authorization message to the payment gateway.
The payment gateway sends an authorization message to the merchant's website, indicating that the payment has been approved.
The merchant's website processes the order and sends a request to the payment gateway to capture the funds.
The payment gateway sends a request to the payment processor to transfer the funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account.
The payment processor transfers the funds and sends a message to the payment gateway to confirm the successful transfer.
The payment gateway sends a confirmation message to the merchant's website.
Throughout this process, the payment gateway encrypts the transaction data to protect it from unauthorized access.
Payment gateways use secure sockets layer (SSL) or transport layer security (TLS) protocols to encrypt the transaction data and protect it during transmission. These protocols use a combination of hardware and software to create a secure connection between the merchant's website and the payment processor.
In addition to encrypting the data, payment gateways also perform other security measures to protect against fraud. These measures may include verifying the customer's billing address, checking for suspicious activity, and using risk scoring to evaluate the transaction.
Some payment gateways also offer additional features to merchants, such as the ability to store customer payment information for future transactions, support for recurring billing, and the ability to process refunds.
Finally, payment gateways may charge fees for their services, which may include a per-transaction fee, a monthly fee, and/or a setup fee. These fees can vary significantly depending on the payment gateway and the merchant's business needs.
When a customer places an order on a merchant's website, the payment gateway works behind the scenes to process the payment and transfer the funds from the customer to the merchant. Here's a summary of the process:
The customer enters their payment information on the merchant's website and submits their order.
The merchant's website sends a request to the payment gateway to process the payment.
The payment gateway sends a request to the payment processor to verify the payment method and check for sufficient funds.
If the payment is approved, the payment processor sends an authorization message to the payment gateway.
The payment gateway sends an authorization message to the merchant's website, indicating that the payment has been approved.
The merchant's website processes the order and sends a request to the payment gateway to capture the funds.
The payment gateway sends a request to the payment processor to transfer the funds from the customer's account to the merchant's account.
The payment processor transfers the funds and sends a message to the payment gateway to confirm the successful transfer.
The payment gateway sends a confirmation message to the merchant's website, and the transaction is complete.
Are payment gateways regulated in the USA?
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) that enables the transfer of money between two bank accounts using a smartphone. UPI-based payment gateways allow merchants to accept payments from customers using UPI as a payment method.
Here's how a UPI-based payment gateway works:
The customer selects UPI as the payment method on the merchant's website or mobile app.
The merchant's website or app sends a request to the payment gateway to initiate a UPI payment.
The payment gateway sends a request to the NPCI's UPI servers to create a payment request.
The NPCI's servers create a payment request and send it to the customer's bank.
The customer's bank sends the payment request to the customer's smartphone via their UPI app.
The customer reviews the payment request and, if everything is correct, approves the payment using their UPI PIN.
The customer's bank sends a message to the NPCI's servers to confirm the payment.
The NPCI's servers send a confirmation message to the payment gateway.
The payment gateway sends a confirmation message to the merchant's website or app, indicating that the payment has been completed.
Throughout this process, the UPI payment gateway ensures that the transaction is secure and that the funds are transferred safely between the customer's and merchant's bank accounts.
Are payment gateways regulated in the USA?
Which payment gateways offer white-label solutions in the USA?
White-label solutions are payment gateway products or services that are branded and customized to match the look and feel of a merchant's website or business. Some payment gateways that offer white-label solutions in the United States include:
Stripe: Stripe offers a white-label payment gateway called Stripe Terminal that can be customized with a merchant's logo and colors.
PayJunction: PayJunction offers a white-label payment gateway called PayJunction Tranz that can be customized with a merchant's branding.
Braintree: Braintree, a subsidiary of PayPal, offers a white-label payment gateway called Braintree Marketplace that can be customized with a merchant's branding.
Authorize.Net: Authorize.Net offers a white-label payment gateway called Authorize.Net SIM that can be customized with a merchant's branding.
NMI: NMI offers a white-label payment gateway called NMI Gateway that can be customized with a merchant's branding.
It's worth noting that white-label solutions may come at an additional cost and may require the merchant to have a certain volume of transactions or meet other requirements.
Related Post :

Comments
Post a Comment